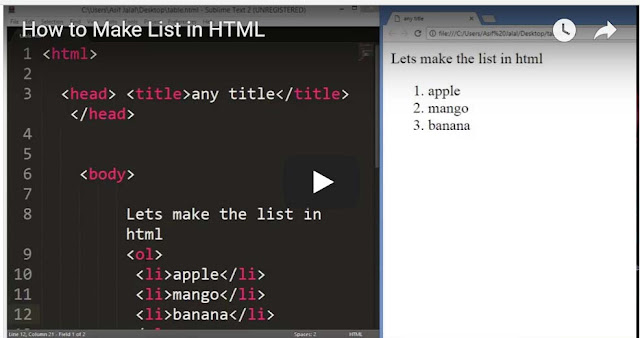
Before we look at the another concepts used to build Websites it is important to consider the Different ways in which people access the web And clarify some terminology
Browsers
People access websites using software called a web browser. Popular examples include Firefox, Internet
Explorer, Safari, Chrome, and Opera. In order to view a web page, users might
type a web address into their browser, follow a
Link from another site, or use a bookmark. Software
manufacturers regularly release new versions of browsers with new features and
supporting new additions to languages. It is important, however, to remember
that many computer owners will not be running the latest versions of these
browsers. Therefore you cannot rely on all visitors to your site being able to
use the
Latest functionality offered in all browsers.
Web Servers
When you ask your browser for a web page, the
request is sent across the Internet to a special computer known as a web server
which hosts the website. Web servers are special computers that are constantly connected
to the Internet, and are optimized to send web pages out to people who request
them.
A Web server is a program that uses HTTP
(Hypertext Transfer Protocol) to serve the files that form Web pages to users,
in response to their requests, which are forwarded by their computers' HTTP
clients. Dedicated computers and appliances may be referred to as Web servers
as well.
The process is an example
of the client/server model. All computers that host Web sites must have Web
server programs. Leading Web servers include Apache (the most widely-installed Web
server), Microsoft's Internet Information Server (IIS) and nginx (pronounced
engine X) from NGNIX. Other Web servers include Novell's NetWare server, Google
Web Server (GWS) and IBM's family of Domino servers

Web servers often come as part of a larger
package of Internet- and intranet-related programs for serving email,
downloading requests for File Transfer Protocol (FTP) files, and building and
publishing Web pages. Considerations in choosing a Web server include how well
it works with the operating system and other servers, its ability to handle
server-side programming, security characteristics, and the particular
publishing, search engine and site building tools that come with it.
The Main Purpose of a Web Server
A web server’s main
purpose is to store web site files and broadcast them over the internet for you
site visitor’s to see. In essence, a web server is simply a powerful computer
that stores and transmits data via the internet. When someone visits a web page
on your site their browser communicates with your web server, sending and
receiving information that ultimately dictates what appears on the visitor’s
computer screen. Thus, the main purpose of a web server is to store and
transfer web site data upon the request of a visitor’s browser.
Why Are Web Servers
Needed?
Without web servers the
internet as we know it would cease to exist. Web servers are an integral part
of the way the internet works. The web hosting industry is simply used to lease
out web servers, providing average business owners and individuals with the
opportunity to use high-tech servers that make it possible to expand their
outreach to the entire world. Without rental web servers the internet would be
a fraction of the size it is today, as most web site owners can afford to buy
their own web server in cash.
Web servers are the
gateway between the average individual and the world wide web, yet surprisingly
web hosting plans start at only a couple of dollars per month. Now that you’re
familiar with web servers you can begin shopping for a quality web hosting plan
without the usual confusion that most novices experience.
Some big companies run
their own web servers, but it is more common to use the services of a web
hosting company who charge a fee to host your site.
There are many type of server available.
-Shared Hosting
Shared Hosting is widely
used as “Web Server”. It’s usually way cheaper than its dedicated counterpart.
Basically, you’re getting an account into the host control panel, thus allowing
multiple website to run on a SINGLE server. This solution is mostly used for
web development, blogging and or personal websites (low traffic). It doesn’t
scale very well if you need additional resources (limited hardware) and you
could be affected by noisy neighbors; businesses overselling hardware and/or
other user using too much resources on the server, affecting your overall
performance.
-VPS/Cloud Server
Cloud servers are
based on virtualization technology. In simple terms, you get a fraction (CPU,
RAM, and Storage) of a clustered infrastructure. These “Virtual Machines” can
independently host their own operating system, creating a virtual private
environment/server. These systems cost a fraction of the price of a Dedicated
Server, because, again, you’re sharing with multiple users. This VPS/Cloud is
scalable, allowing users to scale up their infrastructure and resources (CPU,
RAM, and Storage), on-demand. This solution is also mostly used for web
development, blogging, personal websites, e-commerce and web applications.
-Dedicated Server
A dedicated server or
Bare Metal Server is a physical server. With a dedicated server you control all
of the server’s resources (CPU, RAM, and Storage) and you won’t be affected by
noisy neighbor. This type of solution is robust and particularly useful for
large websites (High Traffic, ecommerce), intranet, virtualization/private
cloud (VPS/Containers), etc. They usually cost more than Cloud /VPS, but offer
a better performance/$ ratio if the extra performance is required.
Summarize what we explained here
A Server, in general, is a piece of software
running on a machine that serves client’s requests (Through any protocol, Tcp,
HTTP… ) , those requests could be calculating a value, retrieving some data,
inserting some data, deleting some data, or anything you can think about. The
returned data could be represented in many ways, most commonly XML, JSON, HTML.
A Web Server is not
different at all, it is more specialized to serve web pages (HTML content,
javascript, css, or anything related), through HTTP protocol.
Devices
People are accessing websites on an increasing range of devices including
desktop computers, laptops, tablets, and mobile phones. It is important to remember
that various devices have different screen sizes and some have faster
connections to the web than others.
Screen readers
Screen readers are programs that read
out the contents of a computer screen to a user. They are commonly used by
people with visual impairments. In the same way that many countries have legislation that require public buildings to be accessible to those with disabilities, many laws have also been passed that require
websites be accessible to those with disabilities. Throughout this book you
will see several references to screen readers.
These notes will help ensure
that the sites you create are accessible to people who use such software. It is interesting to note
that technologies similar to those employed by screen readers are also being
used in other areas where people are unable read a screen, such as when they
are driving or jogging.
Thanks for your time....
if you like my post then you can subscribed my blogger on right side bar area by putting your email address and hit subscribed button to get connected with my blogger. you can also like my blogger using Facebook button on right sidebar just bellow the email subscription.
Thanks for your time....